Explore the best eco-friendly building materials for your 2024 home renovation in India. From recycled steel to terracotta tiles, discover their benefits, costs, and DIY suitability. Create a sustainable home while reducing your carbon footprint.
In the wake of global environmental concerns, the construction industry in India is undergoing a significant shift towards sustainability. Homeowners are increasingly opting for eco-friendly building materials not only to reduce their carbon footprint but also to enjoy tangible benefits like lower energy bills and a healthier living environment. This blog post serves as your comprehensive guide to the top 10 eco-friendly building materials for your 2024 home renovation in India, providing detailed insights into their benefits, considerations, availability, and DIY suitability.
1. Recycled Steel: Strength in Sustainability
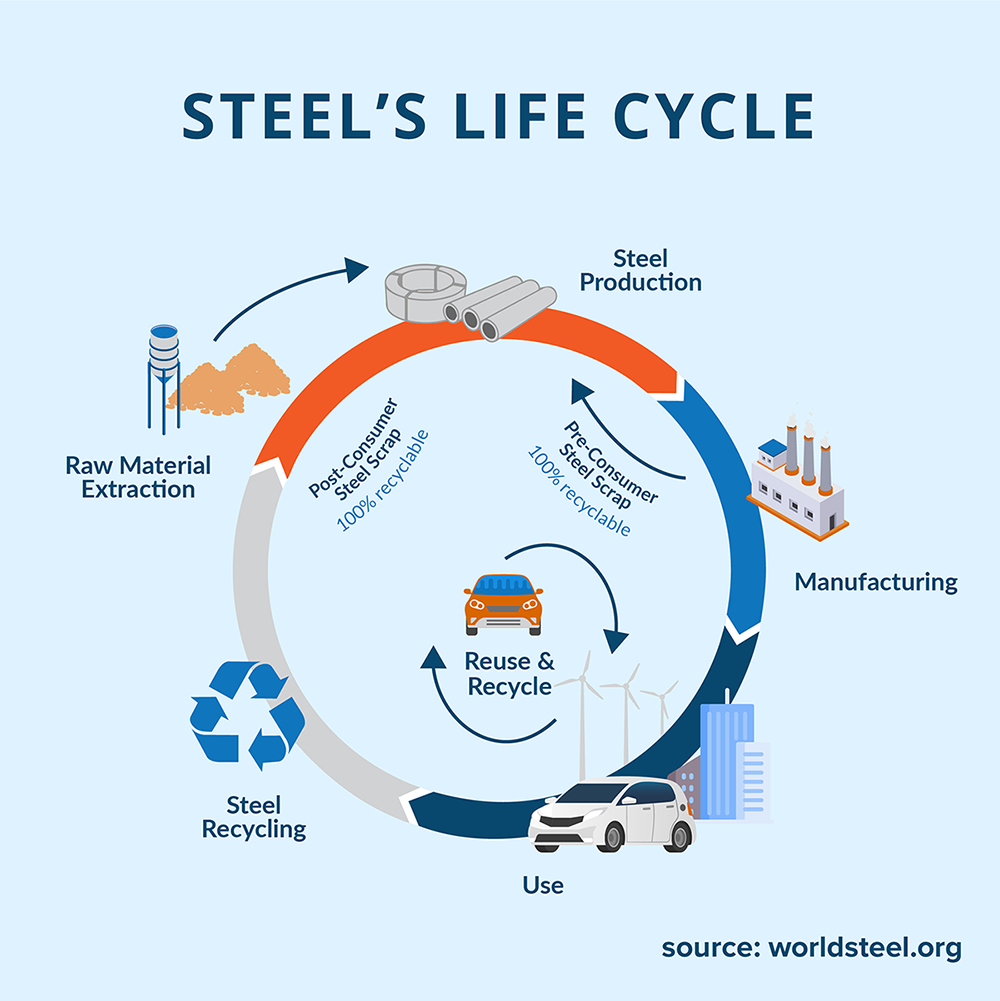
Benefits:
- Environmental Impact: Recycled steel significantly reduces reliance on energy-intensive virgin steel production, making it a sustainable choice for construction projects.
- Strength and Durability: Despite being recycled, steel maintains exceptional strength and durability, ensuring longevity and structural integrity.
- Low Maintenance: Unlike some traditional building materials, recycled steel requires minimal maintenance over its lifespan.
Considerations:
- Specialized Installation: Installing recycled steel necessitates specialized skills and equipment, which may add to the overall project cost.
- Limited Sizes and Shapes: Availability of recycled steel products in specific sizes and shapes may be more restricted compared to virgin steel options.
Time & Resources:
- High Requirements: Professional installation is essential, and lead times may vary depending on availability and project specifications.
Cost:
- Varies: The cost of recycled steel can vary based on the type of product and supplier, generally leaning towards being more expensive than virgin steel.
Availability (India):
- High: Recycled steel products are increasingly accessible from major steel manufacturers across India, contributing to their growing popularity in sustainable construction projects.
DIY Friendly?
• No: Due to the specialized skills and equipment required, handling and installing recycled steel is not recommended as a DIY project.
2. : Nature’s Versatile Resource
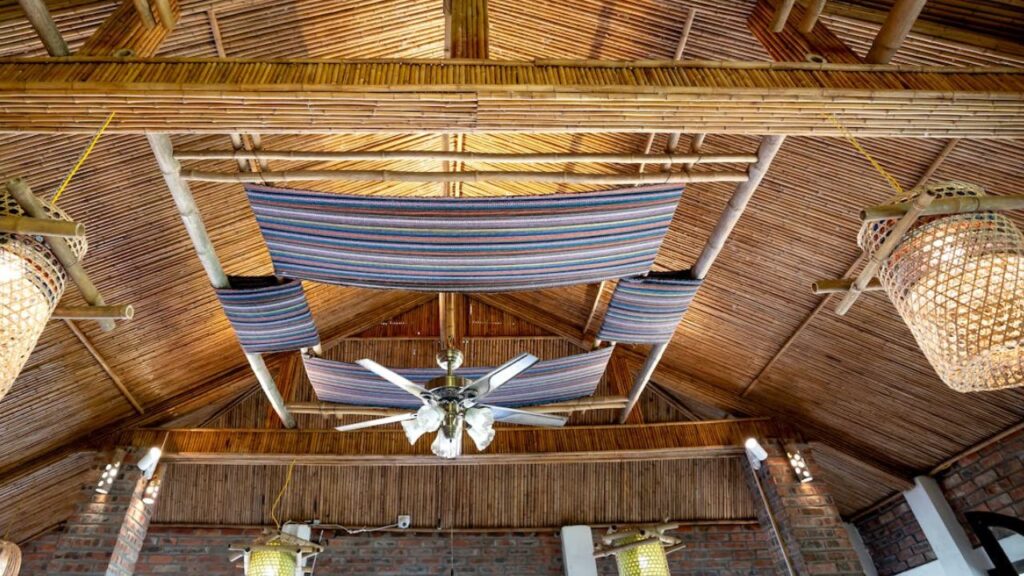

Benefits:
- Renewable and Fast-Growing: Bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional hardwoods.
- Strength and Insulation: Despite its lightweight nature, bamboo boasts an impressive strength-to-weight ratio and offers natural insulation properties.
- Versatility and Aesthetic Appeal:
Bamboo is a versatile material suitable for various applications, and its natural beauty adds an aesthetic charm to any space.
Considerations:
- Treatment Requirements: Proper treatment is essential to prevent issues like warping and insect infestation, particularly in humid climates.
- Availability: While bamboo is abundant in India, availability of treated bamboo products may vary by region.
Time & Resources:
- Moderate Requirements: Construction with bamboo can be faster than traditional methods, but skilled labor may be necessary for certain projects.
Cost:
- Varies: The cost of bamboo depends on factors such as type, treatment, and sourcing, generally making it more affordable than hardwood options.
Availability (India):
- High: India’s status as a major producer of bamboo ensures its widespread availability and affordability for construction projects.
DIY Friendly?
- Yes (with limitations): Basic projects like fencing can be DIY-friendly, but more complex applications may require professional carpentry skills.
3. Earthen Plasters: Natural Temperature Regulators
Benefits:
- Natural Regulation: Earthen plasters are breathable materials that naturally regulate indoor temperature and humidity levels, contributing to a comfortable living environment.
- Local Sourcing: Often sourced locally, earthen plasters minimize environmental impact and support regional economies.
- Health Benefits: With no harmful chemicals or VOCs, earthen plasters promote indoor air quality and overall well-being.
Considerations:
- Application Techniques: Proper application techniques are essential for achieving desired results, and certain climates may be more suitable for earthen plasters than others.
- Drying Time: Earthen plasters may have a longer drying time compared to conventional alternatives, requiring patience during the construction process.
Time & Resources:
- Moderate Requirements: While the materials are readily available, applying earthen plasters effectively may require some training or skilled labor.
Cost:
- Low to Medium: Earthen plasters are generally budget-friendly compared to conventional materials, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious homeowners.
Availability (India):
- High: Abundant raw materials for earthen plasters can be found throughout India, ensuring accessibility for construction projects.
DIY Friendly?
- Yes: With available workshops and online resources, earthen plasters can be a rewarding DIY project for those willing to invest time in learning the application techniques.
Also Read From Pilgrimage Path To Investment Paradise 2024! Shri Ram Mandir Explodes Real Estate Boom In Ayodhya! A Complete Investor’s Guide
4. Reclaimed Wood: Sustainable Stories in Every Plank
Benefits:
- Forest Conservation: Reclaimed wood reduces the demand for virgin timber, promoting forest conservation and biodiversity.
- Unique Aesthetic: Each piece of reclaimed wood tells a story, adding character and charm to any space with its unique patina and history.
- Environmental Footprint: By repurposing existing materials, reclaimed wood minimizes waste and contributes to a circular economy.
Considerations:
- Condition and Treatment: Depending on its condition, reclaimed wood may require repairs, cleaning, or treatment before use in construction projects.
- Limited Availability: Sizes and types of reclaimed wood may be more limited compared to commercially available lumber options.
Time & Resources:
- Moderate Requirements: Renovation projects using reclaimed wood may take slightly longer due to variations in size and condition.
Cost:
- Varies: The cost of reclaimed wood can vary based on factors such as type, condition, and sourcing, generally making it more affordable than new wood options.
Availability (India):
- Moderate: While availability is increasing from salvage yards and architectural dismantlers, reclaimed wood may still be less accessible compared to conventional lumber.
DIY Friendly?
- Yes (with carpentry skills): Basic projects like wall paneling may be DIY-friendly, but more complex applications require carpentry expertise for cutting, fitting, and finishing.
5. Terracotta Tiles: Timeless Elegance for Sustainable Flooring
Benefits:
- Durability and Heat Resistance: Terracotta tiles are known for their durability and heat resistance, making them suitable for various indoor and outdoor applications.
- Local Sourcing: Often sourced locally, terracotta tiles reduce transportation footprints and support local economies.
- Timeless Aesthetic: With various designs and finishes available, terracotta tiles add timeless elegance to any space, enhancing its visual appeal.
Considerations:
- Fragility: Terracotta tiles are relatively brittle and require careful handling during installation to prevent chipping or cracking.
- Professional Installation: While basic tiling projects may be attempted by DIY enthusiasts, professional installation is recommended for a flawless finish.
Time & Resources:
- Moderate Requirements: Skilled labor may be needed for achieving a professional finish, particularly in intricate or large-scale projects.
Cost:
- Varies: The cost of terracotta tiles depends on factors such as size, design, and origin, generally making them more affordable than high-end imported tiles.
Availability (India):
- High: Terracotta is a traditional Indian material widely available across the country, ensuring accessibility for construction projects of all scales.
DIY Friendly?
- No: While a skilled DIYer might attempt basic tiling projects, professional installation is recommended to ensure proper leveling and grouting for long-lasting results.
Here’s a table summarizing the information provided for each eco-friendly building material:
| Eco-Friendly Building Material | Benefits | Considerations | Time & Resources | Cost | Availability (India) | DIY Friendly? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Steel | – Reduces reliance on energy-intensive production – Exceptional strength and durability – Low maintenance | – Specialized installation required – Limited sizes and shapes compared to virgin steel | High | Varies based on type | High | No |
| Bamboo | – Renewable and fast-growing – Strength and insulation properties – Versatility and aesthetic appeal | – Treatment requirements – Limited availability of treated bamboo | Moderate | Varies depending on type and treatment | High | Yes (with limitations) |
| Earthen Plasters | – Natural regulation of indoor temperature and humidity – Local sourcing – Health benefits | – Specific application techniques required – Longer drying time compared to conventional plasters | Moderate | Low to Medium | High | Yes |
| Reclaimed Wood | – Promotes forest conservation – Unique aesthetic – Environmental footprint reduction | – Condition and treatment considerations – Limited availability compared to new wood | Moderate | Varies depending on condition | Moderate | Yes (with carpentry skills) |
| Terracotta Tiles | – Durability and heat resistance – Local sourcing – Timeless aesthetic | – Fragility during installation – Professional installation recommended | Moderate | Varies depending on size and design | High | No |
Stay tuned for Part 2 of this blog post, where we’ll explore five more eco-friendly building materials to empower your sustainable renovation journey.
READ PART-2 10 Eco-Friendly Building Materials In 2024 That Will Transform Your Home Renovation In India (Part-2)
With these eco-friendly building materials, you can breathe easy and live green while creating a home that not only benefits the environment but also enhances your quality of life. Let’s embark on this journey towards a greener future, one sustainable brick at a time.